|
National Toxicology Program
National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences US Department of Health and Human Services November 29, 2018 Re: Nomination for research on the heritable (germ cell) effects of general anesthetic agents Dear NTP: Each year in the United States 1.5 million young children and an unknown number of fetuses are acutely exposed to important and necessary, yet neurotoxic and epigenetically potent chemicals—general anesthetic gases (GA). While there has been ample research on somatic effects of these agents, there has been little attention to germ cell, or heritable, effects of exposure during critical windows of germline development. This represents a shocking void in the research, given that it is established that GA can cause substantial changes in gene and protein expression, and that animal models have consistently demonstrated intergenerational behavioral and learning impairment. Furthermore, in my experience as a leader in the autism community and as a research philanthropist, I have detected alarming patterns of neurodevelopmental pathology in offspring of parents who were heavily exposed to GA in very early life, during vulnerable periods of gametogenesis. (1) GA causes epigenetic modification of the genome It has been known for some time that general anesthetics induce epigenetic modification of the genome. General anesthesia includes agents such as isoflurane, enflurane, halothane, and sevoflurane not only influence neuronal function, they also induce epigenetic alterations such a chromatin changes, histone modifications and shifts in DNA methylation. (Csoka et al., 2009; Vutskits et al., 2018). GA agents can cause apoptosis and amyloid beta-protein accumulation, and neuronal damage, with potential mechanisms including enhanced protein misfolding and aggregation (Csoka et al., 2009). It has been shown that GA can cause substantial changes in gene and protein expression (Pan et al., 2009; Rampil et al., 2006). For example, even brief exposure to isoflurane leads to widespread changes in genetic control in the amygdala six hours after exposure (Pan et al., 2006). GA can modulate histone acetylation and as such may have deleterious effects on transcription of genes crucial for proper synapse formation and cognitive development (Dalla Massara et al., 2016). A recent study on sevoflurane demonstrated the induction of DNA methylation modification and changes in expression go brain-relevant genes. The investigators found a sex-specific decrease in KCC2 and increased DNA methylation of the KCC2 gene promoter in the sperm of F0 exposed sires (Ju et al., 2018). Germ cells are at heightened sensitivity to epigenomic error during the early phases of gametogenesis (fetal and neonatal periods) when the DNA is globally demethylated and then remethylated in a sex-dependent manner. Abnormal patterning of DNA methylation or chromatin architecture in a particular region of germline in the developing fetus or neonate could lead to dysregulated somatic development in the generation borne of those exposed germ cells. This is not mere speculation. Empirical evidence supports this idea. (2) Mammal models demonstrate intergenerational toxicity [Note F2 = autistic child; F1= parent; F0 = gestating mother of F1 and grandmother of F2.] The three mammal studies published on the question all point in the same direction. Most recently, neonatal exposure to the widely used general anesthetic agent sevoflurane (sub-clinical doses, in this case) affected the brains and behavior of the next generation of male rats through epigenetic modification of gene expression, while F1 females were at diminished risk (Ju LS, et al. 2018). The implications of this finding could be significant. To quote an accompanying editorial, ““Hence, we are faced with a real possibility that general anaesthetics are not innocuous agents that ‘only put children to sleep’ but rather formidable modulators of chromatin remodeling and function…. The current study extends previous reports of sex differences by showing that anaesthetic exposure itself can alter expression of chloride channels in certain brain regions and that this effect is heritable from exposed male parents to unexposed offspring” (Vutskits et al., 2018). The two earlier studies to observe offspring impairment are from the 1980s, well before epigenomic or chromatin mechanisms were under consideration. Learning retardation was seen in F2 mouse offspring of F1 parents exposed to general anesthesia in utero—in other words, mental impairment in the grandpups of the exposed gestating dams (Chalon et al., 1981). This phenomenon was also seen with the sires were exposed in adulthood. The general anesthetic agent enflurane administered to male mice was found to adversely affected learning function of their offspring (Tang et al., 1985). (3) Autism family case studies suggest GA acts as a potent germline toxicant during sensitive periods of gametogenesis For several years I have been discussing the question of parental fetal or early life exposures with autism parents. After numerous interviews I perceived a strong pattern of F2 pathology where the F1 had an early life exposure to GA, often by virtue of repeated and complicated surgeries. (a) F0 gestational exposure. These are cases where the F0 grandmother of the F1 parent, male or female, had surgery during gestation with the F1. Reasons for the F0 surgeries during pregnancy included an appendectomy, surgery following an automobile accident, and surgery to correct a problem with the placenta. When an F1 parent had this prenatal exposure, he or she often had multiple F2 offspring, male and female, with autism. From a biological point of view this multiplex phenomenon would make sense because the early germ cells at this stage would likely be similarly exposed. (b) F1 early childhood exposure. These are cases where the F1 parent, male or female, had surgery or a series of surgeries, in early life. Reasons for the F1 surgeries included tumor removal, hernia repair, surgeries to correct heart defects, and surgeries to correct birth defects such as clefts and club foot. When an F1 parent had this early life exposure, I saw he or she often had multiple F2 offspring, male and female, with autism. From a biological point of view this multiplex phenomenon might also make sense because the female oogonia are undergoing imprinting through the first year and are not yet mature, and the pre-meiotic male spermatogonial stem cells could also retain errors in their later-differentiated spermatocytes. (c) F1 paternal pre-puberty/puberty exposure. These are cases where the F1 father had a series of surgeries around the time of puberty and beyond. In this category, two stories jump out. I have two male friends who suffered gunshot wounds in late childhood. Both underwent multiple surgeries in puberty and beyond to correct extensive damage. They each have one F2 son with extremely severe autism. Actually the word autism does not do their phenotypes justice, as their conditions are catastrophic, involving profound intellectual disability and severe behaviors, including in one case continuous and extreme self-injurious behaviors. In both of these cases the father also has F2 children who are typically developing. From a biological point of view this simplex phenomenon perhaps make sense because the germ cells were affected at a later stage of differentiation. I am aware these are all anecdotes and alone prove nothing. But it is worth nothing that in these cases, the families had no history of autism, and to my knowledge, the families and children had no risk factors for autism. As a rough control group, I noticed that where the F1 parent’s siblings did not have these sorts of surgical exposures, the F2s were typically developing. In spite of the importance of the questions presented, the NTP might respond, “we only study environmental chemicals, and GA falls under the purview of the FDA, not the NIEHS.” In spite of that, I entreat the NTP to include these exposures in the NTP for the following reasons:
The question remains: which agents to study? Because halothane was the most popular GA during the post-war decades and sevoflurane is popular today, I would suggest the NTP begin with those two agents and then expand to others depending on the signals from pilot data. It may turn out that thorough investigation of germline effects (via many different windows of germline development, many different doses, and/or many different mixtures) may well be warranted. Thank you for your kind consideration of this nomination. Very truly yours, Jill Escher References Chalon J, Tang CK, Ramanathan S, Eisner M, Katz R, Turndorf H. 1981. Exposure to halothane and enflurane affects learning function of murine progeny. Anesth Analg 60:794–7. Csoka AB, Szyf M. Epigenetic side-effects of common pharmaceuticals: A potential new field in medicine and pharmacology. 2009. Med. Hypoth. 73;770–780. Dalla Massara L, Osuru HP, Oklopcic A, et al. General anesthesia causes epigenetic histone modulation of c-fos and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, target genes important for neuronal development in the immature rat hippocampus. 2016. Anesthesiology 124:1311e27. Heflich R. 2018. Lecture at Environmental Mutagenesis and Genomics 2018 Meeting, “My Forty Years at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Robert H. Heflich, U.S. Food and Drug Administration.” Delivered September 24, 2018. Ju LS, Yang JJ, Morey TE, Gravenstein N, Seubert CN, Resnick JL, Zhang JQ, Martynyuk AE. 2018. Role of epigenetic mechanisms in transmitting the effects of neonatal sevoflurane exposure to the next generation of male, but not female, rats. Brit J Anesth 121:2;406-4168. Martinez et al., Thyroid hormone influences brain gene expression programs and behaviors in later generations by altering germ line epigenetic information, Mol. Psych. 2018. Pan JZ, Wei H, Hecker JG, Tobias JW, Eckenhoff RG, Eckenhoff MF. Rat brain DNA transcript profile of halothane and isoflurane exposure. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2006;16:171–82. Rampil IJ, Moller DH, Bell AH. Isoflurane modulates genomic expression in rat amygdala. Anesth Analg 2006;102:1431–8. Tang CK, Chalon J, Markham JP, Ramanathan S, Turndorf H. Exposure of sires to enflurane affects learning function of murine progeny. 1985. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 5:2,67. Vutskits L, Sall JW, Jevtovic-Todorovic V. A poisoned chalice: the heritage of parental anaesthesia exposure. 2018. Brit. J. Anesth. 121;2,337-339. Woodcock, J. Letter to Escher in response to citizens petition to withdraw approval for 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate as a drug used in pregnancy. 2018. http://www.germlineexposures.org/uploads/6/4/0/9/6409433/fda-2015-p-0876.pdf (accessed November 9, 2018).
0 Comments
[This rehashes a previous blog entry from 2014.]
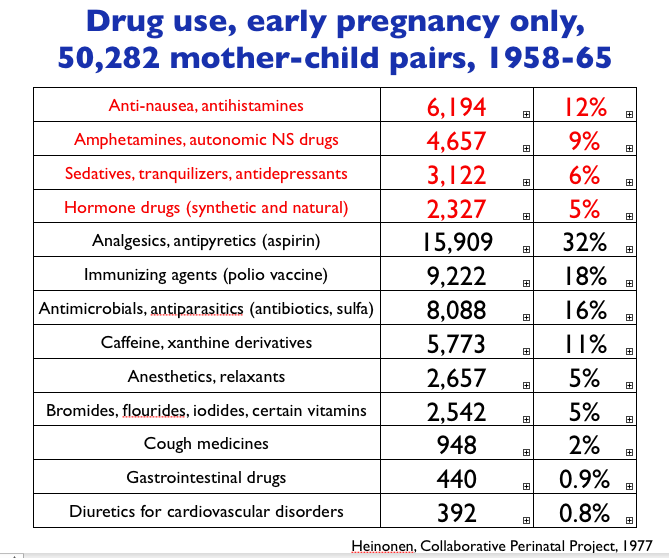
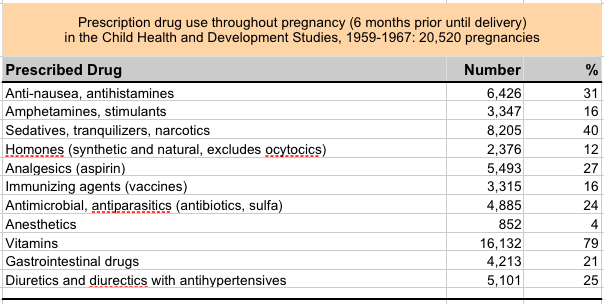
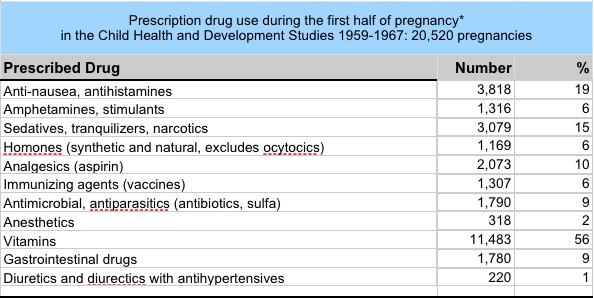
By Jill Escher How pervasive was pregnancy drug use in the 1960s? We can look at two cohorts, the CHDS (Child Health and Development Studies) and the CPP, or Collaborative Perinatal Project to get a sense of this vast history. The top chart shows CHDS drug use throughout pregnancy, and the bottom two refer to drug CHDS and CPP drug use in roughly the first half of pregnancy. Use of anti-nausea drugs, sedatives, hormones, painkillers and amphetamines were all common. Which of these abnormal exposures entered the womb and fetal tissue? All of them. Which of these affected fetal development? Most of them, though sometimes very subtly. Which of them affected fetal germline? Well, we hope to find out. Escher Fund for Autism
1590 Calaveras Avenue San Jose, CA 95126 Francis Collins, Director, National Institutes of Health Diana Bianchi, Director, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Joshua Gordon, Director, National Institute of Mental Health Linda Birnbaum, Director, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Via Email and U.S. Mail November 4, 2018 Re: Request for NIH research program on the heritable effects of general anesthesia Dear Drs. Collins, Bianchi, Gordon and Birnbaum: Let me start this missive by acknowledging that you probably receive a number of letters from community members opining about potential sources of the increasing prevalence of autism and related disorders. Now in my seventh year of funding pilot studies relating to autism, I have grown to share the research community’s skepticism toward the out-of-the-box ideas regarding causation, because, well, most of those ideas are just plain wrong. However, I am writing today about a very particular concept that has leapt out at me as deserving serious attention at the NIH: the question of heritable, germline-borne effects of agents of general anesthesia. My work as a funder of pilot studies in non-genetic inheritance began nearly seven years ago shortly after I discovered I had been very heavily and continuously exposed in utero to powerful synthetic steroid hormone drugs, prompting the idea that hormone signal disruption to my fetal primordial germ cells could have perturbed the epigenomic programming of my eggs, thus causing dysregulation of gene expression, seemingly limited to the prefrontal cortex, in my two children who have idiopathic nonverbal autism [Escher J, Bugs in the Program: can pregnancy drugs and smoking disturb molecular reprogramming of the fetal germline, increasing heritable risk for autism and neurodevelopmental disorders? Environ. Epigen. 2018;4:2]. To further develop hypotheses regarding non-genetic inheritance in neurodevelopmental disorders, I delved into the scientific literature regarding direct exposures to germline, engaged deeply with the scientific community, and interviewed autism families in an effort to detect patterns regarding parental fetal or early life exposures and adverse outcomes in their children. A few years ago, I noticed a number of stray comments (as I was not asking about surgeries at all at first) that emerged as a strong pattern. Many of the parents made remarks about early exposure to surgery. These stories seemed to fall into three categories. [Here F2 = autistic child; F1= parent; F0 = gestating mother of F1 and grandmother of F2.] (1) F0 gestational exposure. These are cases where the F0 grandmother of the F1 parent, male or female, had surgery during gestation with the F1. Reasons for the F0 surgeries during pregnancy included an appendectomy, surgery following an automobile accident, and surgery to correct a problem with the placenta. When an F1 parent had this prenatal exposure, he or she often had multiple F2 offspring, male and female, with autism. From a biological point of view this multiplex phenomenon would make sense because the early germ cells at this stage would likely be similarly exposed. (2) F1 early childhood exposure. These are cases where the F1 parent, male or female, had surgery or a series of surgeries, in early life. Reasons for the F1 surgeries included tumor removal, hernia repair, surgeries to correct heart defects, and surgeries to correct birth defects such as clefts and club foot. When an F1 parent had this early life exposure, I saw he or she often had multiple F2 offspring, male and female, with autism. From a biological point of view this multiplex phenomenon might also make sense because the female oogonia are undergoing imprinting through the first year and are not yet mature, and the pre-meiotic male spermatogonial stem cells could also retain errors in their later-differentiated spermatocytes. (3) F1 paternal pre-puberty/puberty exposure. These are cases where the F1 father had a series of surgeries around the time of puberty and beyond. In this category, two stories jump out. I have two male friends who suffered gunshot wounds in late childhood. Both underwent multiple surgeries in puberty and beyond to correct extensive damage. They each have one F2 son with extremely severe autism. Actually, the word autism does not do their phenotypes justice, as their conditions are catastrophic, involving profound intellectual disability and severe behaviors, including in one case continuous and extreme self-injurious behaviors. In both of these cases the father also has F2 children who are typically developing. From a biological point of view, this simplex phenomenon perhaps make sense because the germ cells were affected at a later stage of differentiation. Of course these are all anecdotes, and alone prove nothing. But it is worth noting that in these cases, the families had no history of autism, and to my knowledge, the families and children had no risk factors for autism. As a rough control group, I noticed that where the F1 parent’s siblings did not have these sorts of surgical exposures, the F2s were typically developing. More important, though, is the fact that animal models of heritable effects of general anesthesia exposures demonstrate a biological plausibility. Animal models demonstrate biological plausibility While there is surprisingly little literature on heritable effects of general anesthesia—considering that many of the agents commonly used in the 1950s through today are known to be genotoxic and epigenetically disruptive—the three mammal studies published on the question all point in the same direction. Most recently, neonatal exposure to the widely used general anesthetic agent sevoflurane (sub-clinical doses, in this case) affected the brains and behavior of the next generation of male rats through epigenetic modification of gene expression, while F1 females were at diminished risk [Ju LS, et al., Role of epigenetic mechanisms in transmitting the effects of neonatal sevoflurane exposure to the next generation of male, but not female, rats. Brit. J Anesth. 2018;121:2,406-416]. The implications of this finding could be significant. To quote an accompanying editorial, ““Hence, we are faced with a real possibility that general anaesthetics are not innocuous agents that ‘only put children to sleep’ but rather formidable modulators of chromatin remodeling and function…. The current study extends previous reports of sex differences by showing that anaesthetic exposure itself can alter expression of chloride channels in certain brain regions and that this effect is heritable from exposed male parents to unexposed offspring.” [Vutskits L, et al. A poisoned chalice: the heritage of parental anaesthesia exposure. Brit. J Anesth. 2018;121;2,337-339.] The two earlier studies to observe offspring impairment are from the 1980s, well before epigenomic or chromatin mechanisms were under consideration. Learning retardation was seen in F2 mouse offspring of F1 parents exposed to general anesthesia in utero—in other words, mental impairment in the grandpups of the exposed gestating dams [Chalon J, et al. Exposure to halothane and enflurane affects learning function of murine progeny. Anesth. Analg.1981;60:794–7]. This phenomenon was also seen with the sires were exposed in adulthood. The general anesthetic agent enflurane administered to male mice was found to adversely affected learning function of their offspring [Tang CK, et al. Exposure of sires to enflurane affects learning function of murine progeny. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 1985;5:2,67]. When I attended the Environmental Mutagenesis and Genomics Society meeting in September of this year, several scientists, agreeing about the need for a research program regarding these questions, suggested I contact the NIEHS NTP {National Toxicology Project]. When I attended the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories meeting on Germ Cells in October of this year, several of the scientists also saw the value of these questions, and recommended that I suggest a research program to the NICHD. However, with regard to the FDA’s National Center for Toxicological Research, my discussions with Robert Heflich of the NCTR were not promising, as his department appeared to be neither interested in germ cells nor epigenomic disruptions. Accordingly, I write NIH leaders to ask, what will it take to create a research program specifically devoted to these questions of non-genetic inheritance caused by germ cell exposure to agents of general anesthesia in use from the 1950s to today? While I do plan to submit a nomination to the NIEHS NTP on this topic, I feel that that, while possibly a useful avenue, that is alone insufficient to address the great breadth and weight of these questions. Since the 1980s, the United States has experienced a staggering surge in the prevalence of idiopathic neurodevelopmental disorders we tend to label as autism. We know for certain these serious mental disabilities are highly heritable. We also know with reasonable certainty they are not highly genetic in any classic sense [“Genetic factors do not fully account for the relatively high heritability of neurodevelopmental conditions, suggesting that non-genetic heritable factors contribute to their etiology.” Martinez et al., Thyroid hormone influences brain gene expression programs and behaviors in later generations by altering germ line epigenetic information, Mol. Psych. 2018.] In light of that and the foregoing it makes sense to shift some attention to routes of non-genetic inheritance. While I believe that a great many ancestral germline exposures should concern us (my principal focus remains pregnancy drugs), I cannot help but see the germline effects of general anesthesia issue as an unexplored question of dramatic importance for public health that alone should be addressed without delay. If the NIH or any of its branches would take an interest in what I propose. I have several ideas for research programs in both human cohorts and animal models, and would of course be enthusiastic to share them with you. I can be reached at [email protected]. Thank you for your kind consideration of these comments. Very truly yours, Jill Escher Cc via Email: Robert Heflich, FDA; Rosalie Elespuru, FDA; Sharvani Mahadevaraju, NIH; Daniel Camerini-Otero, NIH; Louis Reichardt, Simons Foundation; Thomas Frazier, Autism Speaks |
AuthorJill Escher, Escher Fund for Autism, is a California-based science philanthropist and mother of two children with severe autism, focused on the question of how environmentally induced germline disruptions may be contributing to today's epidemics of neurodevelopmental impairment. You can read about her discovery of her intensive prenatal exposure to synthetic hormone drugs here. Jill is also president of Autism Society San Francisco Bay Area. Archives
July 2021
Categories |
- Home
-
Expert Q&A
- Eva Jablonka Q&A
- Amander Clark Q&A
- Mirella Meyer-Ficca Q&A
- Janine LaSalle Q&A
- Dana Dolinoy Q&A
- Ben Laufer Q&A
- Tracy Bale Q&A
- Susan Murphy Q&A
- Alycia Halladay Q&A
- Wendy Chung Q&A
- Pradeep Bhide Q&A
- Pat Hunt Q&A
- Yauk and Marchetti Q&A
- Emilie Rissman Q&A
- Carol Kwiatkowski Q&A
- Linda Birnbaum Q&A
- Virender Rehan Q&A
- Carlos Guerrero-Bosagna Q&A
- Randy Jirtle Q&A
- Jerry Heindel Q&A
- Cheryl Walker Q&A
- Eileen McLaughlin Q&A
- Carmen Marsit Q&A
- Marisa Bartolomei Q&A
- Christopher Gregg Q&A
- Andrea Baccarelli Q&A
- David Moore Q&A
- Patrick Allard Q&A
- Catherine Dulac Q&A
- Lucas Argueso Q&A
- Toshi Shioda Q&A
- Miklos Toth Q&A
- Piroska Szabo Q&A
- Reinisch Q&A
- Klebanoff Q&A
- Denis Noble Q&A
- Germline in the News
- Science
- Presentations
- About Us
- Blog
Proudly powered by Weebly

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed